Environment Class 09
A BRIEF OVERVIEW OF THE PREVIOUS CLASS AND Q& A SESSION (05:07 PM)
BIODIVERSITY (05:13 PM)
- Ecosystem diversity is the reference to the variety of habitats, ecosystems, and even ecological processes in a given region.
- This ecosystem diversity is influenced by climatic conditions, vegetation characteristics, hydrological characteristics, Habitat characteristics, and also the interaction between life forms and their collective interaction with the environment.
WORLD DISTRIBUTION OF BIODIVERSITY (05:21 PM)
- How does biodiversity occur?/ Lattitudnal gradient of biodiversity
- 1) Tropical regions- The biggest reserves of diversity
-

- Reasons-
- A lot of heat availability, Abundant heat supply because of high air temperature.
- Abundant Water supply/ High rainfall.
- [* Middle latitudes to higher latitudes are exposed to climate extremes i.e. cold to warm. ]
- Middle latitudes + latitudes closer to the Polar region = Variation in geological time = climatic stability. [* This climatic stability helped in the evolutionary process leading to species diversity]
- [* Tropics are free from the ice age and fluctuations in geological time scale. During the ice age, the average temperature of the earth goes below 20 degrees centigrade and the average temperature of the middle latitudes is 30 degrees centigrade, so the tropics will not see the ice age-like conditions. Tropics will always be warm ]
- Within the tropics, Tropical rainforest has rich biodiversity Example- Equatorial forest, Tropical rainforest of the trade wind belt. They cover 7% of the land surface and constitute 50% of biodiversity.
- They are the biggest "Gene Pool" centres in the world.
- 2) Coral reef regions of the tropics
- They are called "Rainforests of the ocean". 25% of the marine food chain is in the coral reefs. There is a concentrated presence of biodiversity.
- 3) Wetlands of the tropical region
- It includes an inter-tidal zone, Estuary, lakes, etc
- They are the richest in ecosystem productivity, and they are rich in biodiversity.
- 41% of the fish population is in wetlands.
- Wetlands cover 7% of the earth's surface area but have 45% of the earth's ecosystem productivity.
- According to a study, called the millennium ecosystem assessment report 2005 wetlands cover 7% of the world's surface but account for 45% of the earth's natural productivity of ecosystems.
BIODIVERSITY HOTSPOTS (05:46 PM)
- It was given by Norman Myers in 1988.
- Criteria
- It should have at least 1500 species of vascular plants (Xylem and Phloem) endemic to the region
- 70% of its natural habitat must be lost.
- Conservation International- It is an NGO.
- Presently there are 36 Biodiversity hotspots, These cover less than 3% of the world's land surface and have 50% of endemic many species and they have roughly, 43% of Birds, Mammals, Reptiles, and Amphibians as endemic to them.
- Most of these hotspots are part of the tropics.
- Biodiversity hotspots of India
- 1) Western Ghat Hotspot-
- The region has 5000 vascular plants, and 1700 are endemic to nature. It has 139 mammal species of which 17 are edmeic, 508 bird species whose 17 are endemic, and 157 reptile species of which 97 are endemic.
-

- This hotspot includes the largest population of Indian elephants. Bengal Tigers, Lion-tailed Macaque, Nilgiri Tahr, Gaur (Indian bison) and Sloth bears.
- 1/3rd of India's plant species are part of this hotspot.
- 2) Indo-Burman Biodiversity hotspot-
- This includes the entire Northeast India except Assam. It includes Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam, Southern China, and the Andaman Islands (* Not Nicobar).
-
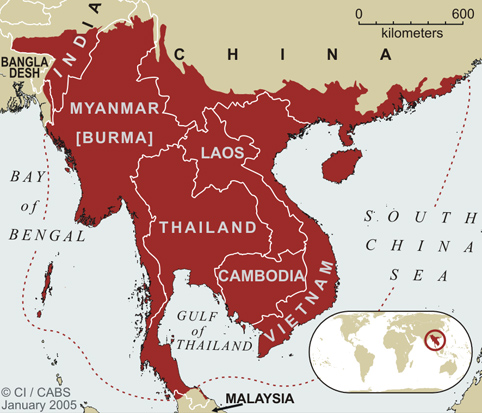
- This hotspot is one of the largest in the area and has a huge population size.
- Life forms- it has 600 globally threatened plants, and 25% of Mammal species of this region are part of the globally threatened. It includes mainly globally threatened bird species which includes one of the rarest birds called the White-eyed river martin.
-
- It has the richest collection of freshwater turtles in the world. Some special species are the Siamese crocodile, The Malayan tiger, the red panda, and the Chinese muntjac, 1300 bird species are part of this hotspot.
- 3) The Himalayan hotspot.
- This includes the Nepal Himalayas, Sikkim Himalayas, Uttarakhand and Himachal Himalayas, Tibet of China, and the Himalayan region of Pakistan.
-
- It includes 163 of many globally threatened species. It also includes Asia's very large animals which are the Asian elephant, Greater One-horned Rhinos, the wild Water Buffalo, the snow leopard, the Himalayan Musk deer, and many species of other deer that are part of this hotspot.
- The Himalayan grasslands have large populations of Bengal Tigers sharing their habitat with the Snow Leopards.
- 10000 plant species, 176 reptile species, 977 bird species, 300 mammals, and 105 Amphibians are part of this hotspot.
- 4) Sunda land
- It consists of southeast regions of Indonesia, Malaysia, The Philippines, Brunei, and the Nicobar Islands of India
-
- [* Borneo Island = Kalimantan part of Indonesia + Sarawak and Sabah part of Malyasia+ Brunei]
- It is the richest hotspot in the world with many species of Vascular plants that include 15000 endemic plant species.
- 770 Bird species, 380 Mammal species, 450 reptiles, 240 Amphibians. The Mammals include the Orangutans which are only found in this hotspot with only 2 species which are Bornean Orangutans and Sumatran Orangutans.
- The short Rhino or Sumatran Rhino which was also part of North-East India earlier is only found in this hotspot.
MEGA BIODIVERSE REGIONS OF THE WORLD (06:35 PM)
- It is given by Conservation International
-
- Criteria
- It should have 5000 endemic plant species
- It should always include coastal ecosystems.
- India is one of the 17 Mega diverse regions of the world.
IMPORTANCE OF BIODIVERSITY (06:53 PM)
- Biodiversity renders services such as
- a) Provisioning services- Supply of foods, medicine, fiber, energy
- b) Regulating services- Regulatig climatic balance, Regulating the hydrological balance
- c) Support services- Support the functioning of the ecosystem
- d) Cultural services- Trees being worshipped, Animals being worshipped, Recreation, tourism, etc.
- Food
- Historically Human has used 7000 plants for their diet [* Identified plants are 2.5 lakhs]. The future supply of food to mankind would be wiped out if we destroy biodiversity.
- Almost all the cultivated plants depend on Bats, Bees, and Birds for pollination. This pollination is important for the development of new species such as Stress resistant, High yield variety, etc.
- Only 30 to 35 plant species account for 95% of plant-based food crops. Only 7000 plant species have been historically used as part of the Human diet. 2.5 lakh species of plants are known to men. The future supply of food plants will have to come from these species which are part of different habitats in their wild.
- Nearly 3/4th of the world's cultivated crops are cultivated by Bees, Birds, and Bats which are part of biodiversity that needs to be conserved.
- Medicines
- Herbs are used as a source of food and Medicines. Plants act as an Antidote for many diseases.
- 95% of the drugs prescribed come from plants and their products. Millions of people who belong to Rural and Indigenous communities almost completely depend on Herbal medicine for a variety of disorders.
- Digitalis, Foxglove provides a lot of products used to make drugs to treat heart disorders. Rosy periwinkle is used in the treatment of cancer.
- Biodiversity provides Water, Energy (Hydropower, Tidal energy, Biomass, Wave energy).
- Regulating services of Biodiversity
- Climatic balance, Hydrological services
- Biodiversity resources regulate climatic balance through the water cycle, oxygen cycle, and carbon cycle.
- 50% of atmospheric oxygen is supplied to the world by Marine plants.
- Regulating the soil formation.
- Supporting services
- It creates support services that support or maintain the functioning of the ecosystem
- Supporting services by protecting the gene pool
- Cultural services
- Indigenous communities take elements of habitat to develop institutions
- They use the Biotic and abiotic elements in the development of cultural institutions, worship, and Rituals
- Ethical dimension for preserving Biodiversity- Humans can not create Biodiversity. Protecting life for the sake of life to exist is the ethical argument for biodiversity conservation.
THREATS TO BIODIVERSITY (07:40 PM)
- Extinction-
- The single biggest threat contributing to the loss of biodiversity.
- [* Urbanization, Industrialization, and population explosion after 1850, Expansion of land for ranching, logging, etc has put up a lot of pressure on the land].
- The cause of extinction is Habitat loss. The reason for habitat loss is humans.
- According to WWF, between 1970 to 2010, the world lost 52% of its biodiversity. The vertebrate population of the earth has been wiped out by 68% over 1970 levels.
- Habitat loss and destruction, therefore, is the single biggest cause of Extinction and Extinction is the single biggest threat to Biodiversity.
- Extinction represents a permanent loss of genetic material to Mankind.
- Today 21% of all Birds, Reptiles, and Fish, 30% of invertebrates and Amphibians, and 22% of all Mammals are faced with the risk of extinction due to habitat destruction.
- Habitat Breakup/ Fragmentation
- Large continuous habitats are fragmented by man and man also destroys wildlife corridors, which are land areas connecting the habitats of the given species.
- These lead to a restricted range for species exposing them to a greater risk of extinction.
- Habitat degradation-
- It means contamination of habitat, reducing the resources i.e. by cutting down trees. Species that are exposed to extinction threats are the most affected when habitat degradation happens.
- This degradation is particularly harmful to vulnerable species.
- Invasive species
- [* Phenotype Plasticity- This is a property that means the capacity of lifeform to adapt to large no of environmental conditions. ]. Invasive species show this property.
- Invasive species can adapt to environmental conditions and multiply very fast.
- Invasive species with their high reproduction rates, high dispersal capacity, and their high phenotype plasticity pose an immediate threat to the local species because they take over their resources.
- Ecologists consider that invasive species are a serious threat to cause the extinction of Amphibians, Reptiles, and Mammals today.
- Excessive exploitation of resources / Indiscriminate exploitation of the resource
- Indiscriminate exploitation of resources like excessive fishery, and excessive logging, because of increasing urbanization, and increasing population in Asia, Africa, and South America is a major threat to biodiversity resources.
- 1/3rd of vertebrates in the world face stress because of indiscriminate exploitation of the resource.
- Shifting cultivation
- It is a threat to biodiversity especially in Tropics.
- Illegal trade in wildlife and products
- It is the 4th biggest trafficked product in the world
- For example- Indian Tiger was almost on the verge of extinction.
The Topics for the next class: Biosphere reserve, Concepts of Water ecology- Wetlands, Mangroves, Estuaries, etc.
